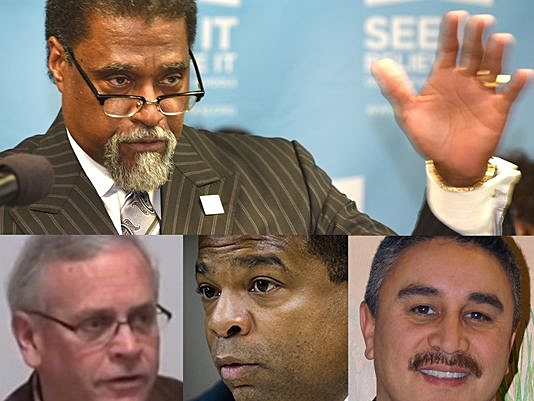
Michigan attorney general Bill Schuette announces charges against four new players, including former Flint emergency managers Darnell Earley and Gerald Ambrose, who were both appointed by Gov. Rick Snyder. Daniel Mears, The Detroit News
Top row: Former emergency manager Darnell Early. Bottom row, from left: Former emergency manager Gerald Ambrose, former Flint Public Works Director Howard Croft and his subordinate, Daugherty Jones. All face criminal charges in the Flint water crisis.(Photo: Detroit News, AP, YouTube)
Flint — Two former emergency financial managers — empowered by state law and appointed by Gov. Rick Snyder’s administration to run Flint — now face criminal charges for actions taken during their tenures that prosecutors say contributed to the city’s water crisis.
A yearlong Michigan Attorney General’s Office investigation into Flint’s water contamination issues has targeted the highest-ranking officials thus far. On Tuesday, investigators announced charges against former emergency managers Darnell Earley and Gerald Ambrose, as well as a pair of former city officials.
That brings the number of government officials charged in the crisis to 13. The probe also focused the harshest spotlight to date on Michigan’s emergency manager law and Snyder’s use of it.
Attorney General Bill Schuette aired harsh criticisms of the emergency manager system — which empowered Earley and Ambrose with broad authority over Flint to address the city’s crumbling finances — Tuesday during a news conference in Flint where he announced the latest charges. In particular, Schuette faulted what he called its “fixation” on financial figures over people as a main factor in creating the city’s long-running water issues.
Full story:www.detroitnews.com, Dec 20 2016